In our increasingly connected and electrified world, lithium batteries have become the bedrock of a wide array of devices, from essential everyday gadgets to the rapidly growing number of electric vehicles. This surge in reliance begs an important question: what happens to these batteries at the end of their life? At Techable.com, we’re actively exploring this pressing issue, revealing how recycling lithium batteries is a critical step not only in waste reduction but also in paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
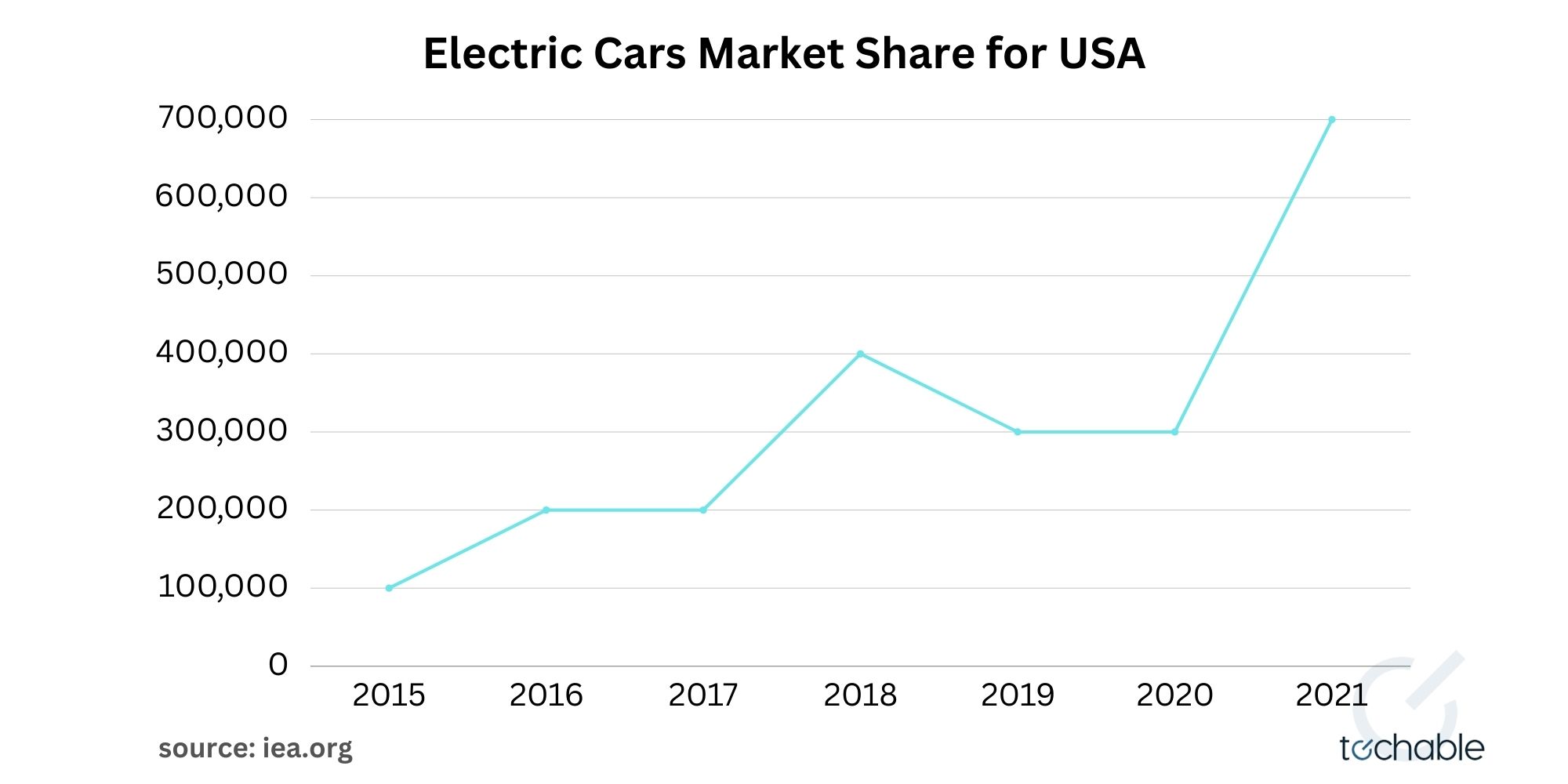
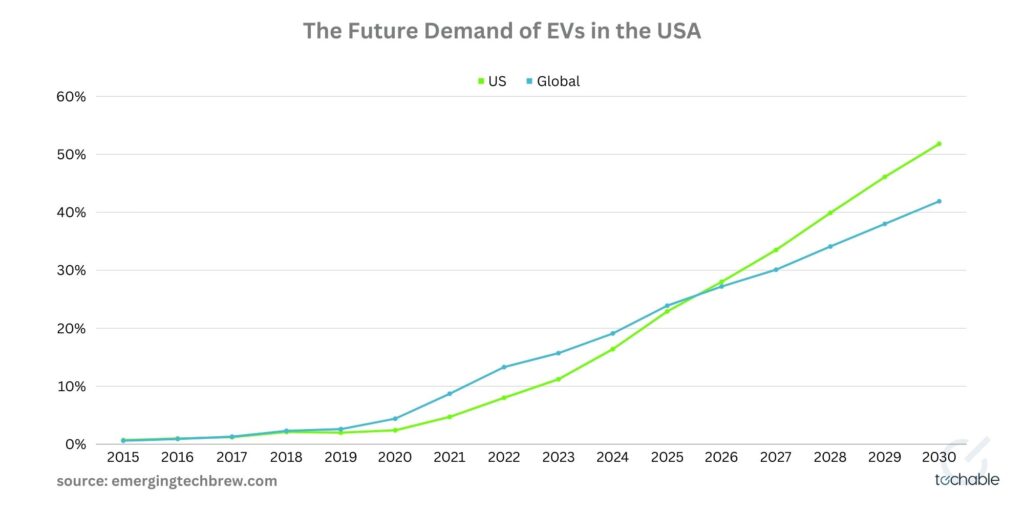
Let’s look at the numbers: by the end of 2021, the global count of electric vehicles – each powered by a lithium battery – exceeded a remarkable 10 million. This trend in lithium battery usage brings to the forefront the need for effective end-of-life management. According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for these batteries is predicted to grow by an impressive 14 times by 2030. This burgeoning demand elevates lithium battery recycling from an environmental imperative to an exciting opportunity to sustainably fulfill our growing energy needs, all while conserving our planet’s natural resources.
The Rise of Lithium Batteries
It all began with their unique ability to store large amounts of energy in a compact size, making them ideal for everything from cell phones to laptops. But the real game-changer has been the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. As of 2021, there were over 10 million electric cars on the road globally, a massive increase from just about 17,000 in 2010. This boom is largely fueled by advancements in lithium battery technology, offering higher efficiency and longer ranges.
The Environmental and Resource Challenge
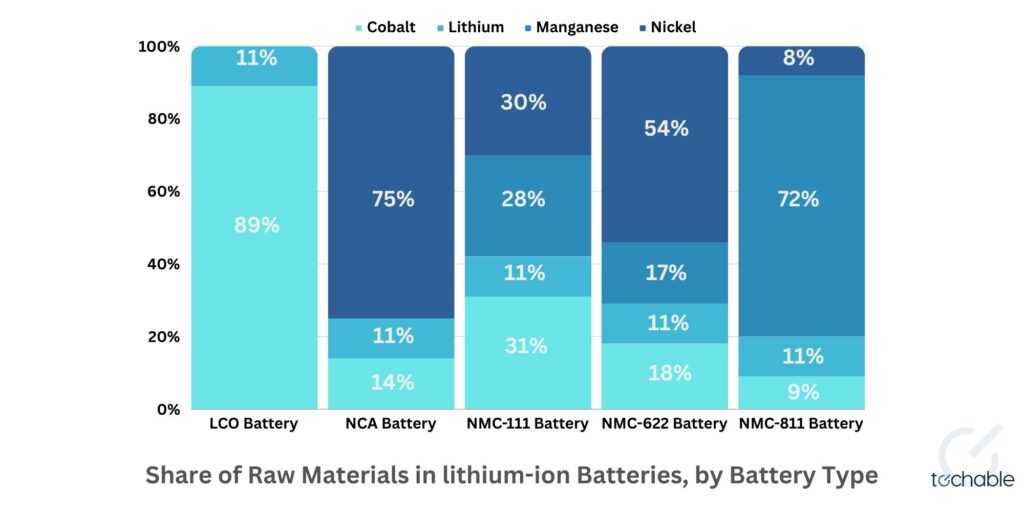
While lithium batteries have been instrumental in driving cleaner transportation and supporting renewable energy storage, their widespread adoption comes with challenges. The extraction and processing of lithium and other associated metals like cobalt and nickel have raised environmental and ethical concerns. Moreover, with the predicted increase in EV sales, the demand for these materials is set to soar. The Global Battery Alliance forecasts that by 2030, the demand for lithium alone could exceed its current supply by almost a factor of two.
We’re not just looking at the rise of lithium batteries as a technological triumph; we’re also acutely aware of the environmental and resource implications that come with it. Understanding this balance is key to navigating the future of energy and ensuring that our solutions are both innovative and sustainable
The Environmental Importance of Recycling
While lithium batteries have powered a greener approach in many sectors, they bring their environmental baggage. Manufacturing these batteries, especially for electric vehicles, involves significant carbon emissions and resource usage. A single electric car battery can produce up to 74% more CO2 during production than manufacturing an internal combustion engine car. Additionally, without proper recycling, spent batteries pose a risk of soil and water contamination due to the toxic and corrosive materials they contain.
Recycling lithium batteries isn’t just about waste management; it’s about creating a sustainable loop in the battery lifecycle. Currently, less than 5% of lithium batteries are recycled globally. This low rate is not only a missed opportunity to reclaim valuable materials but also a significant environmental concern. The need for recycling is further amplified by the projection that the number of spent lithium batteries will surpass 11 million tons annually by 2030.
Effective recycling of lithium batteries is essential for minimizing their environmental impact. It’s about closing the loop – from production to disposal and back again. By fostering a more sustainable approach to battery usage, we can mitigate environmental concerns and pave the way for a truly green energy future.
Current State of Lithium Battery Recycling
Lithium battery recycling, at its core, is about retrieving valuable materials and preparing them for reuse. Presently, there are several practice methods:
Pyrometallurgy: This high-temperature process, often involving temperatures above 1,000°C, is primarily used for recovering metals like cobalt, nickel, and copper. However, it’s less effective for lithium and can pose environmental risks due to the potential release of toxic gases.
Hydrometallurgy: In this approach, chemicals are used to dissolve and extract valuable metals. It’s more effective for lithium recovery but involves complex chemical treatment and recycling processes.
Direct Physical Recycling: Here, components of the battery are directly recycled without the burning or dissolving stages. It’s more environmentally friendly but may not be as effective for all battery types.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite these technologies, lithium battery recycling faces several hurdles. One major challenge is the varying compositions of lithium batteries, which require different recycling methods. Furthermore, the recycling rate for lithium batteries remains low; as of now, only about 5% of all lithium batteries are recycled globally. This low rate is partly due to the lack of infrastructure and the high cost associated with some recycling processes.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing more efficient and sustainable recycling methods. As the demand for lithium batteries grows, so does the necessity for robust recycling systems. The journey towards improved lithium battery recycling practices is complex, but it’s a journey worth taking for a sustainable future. Stay tuned as we continue to explore advancements and innovations in this field.
Technological Innovations in Recycling
The landscape of lithium battery recycling is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations aimed at improving efficiency and environmental impact. Some of the promising technologies include:
Advanced Hydrometallurgical Processes:
Newer chemical methods are being developed to increase the recovery rates of valuable metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt. These processes are becoming more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Enhanced Mechanical Separation: Innovations in mechanical recycling are improving the separation of battery components, leading to better recovery of materials with less environmental impact.
Closed-Loop Recycling:
This approach focuses on recovering and directly reusing materials from old batteries in new batteries. It’s a game-changer in creating a sustainable lifecycle for lithium batteries.
The Impact of Innovations These technological advancements are making significant strides. For instance, new hydrometallurgical processes can now recover up to 95% of lithium, nickel, and cobalt from spent batteries. Additionally, closed-loop recycling initiatives are gaining traction, with some companies already successfully repurposing materials for new batteries.
We recognize these technological strides as crucial in addressing both the environmental and economic challenges of lithium battery recycling. By improving recycling efficiency and material recovery, these technologies not only mitigate environmental impacts but also bolster the supply chain for battery production. Our continuous exploration and reporting on these innovations underscore our commitment to keeping our readers informed about the future of sustainable energy solutions.
Economic and Market Implications
A Growing Market Opportunity. The global market for lithium battery recycling is expanding rapidly. It’s projected to reach $18.1 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 19.6% from 2021 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing awareness of sustainable practices and the soaring demand for lithium-ion batteries, especially in the electric vehicle sector.
Profitability Challenges and Solutions Despite the market potential, recycling lithium batteries profitably can be challenging. The cost of recycling can sometimes exceed the value of the materials recovered, particularly for batteries with lower cobalt content. However, advancements in recycling technologies are gradually bridging this gap. New methods are not only more efficient but also capable of recovering a wider range of valuable materials, enhancing the economic viability of the recycling process.
At Techable.com, we believe that the economic aspect of lithium battery recycling is as crucial as the environmental one. An economically sustainable recycling model is essential for the industry’s long-term viability. The rising demand for these batteries, coupled with advancements in recycling technology, presents a significant opportunity for businesses and entrepreneurs. By focusing on innovative and efficient recycling methods, the industry can turn the challenge of battery waste into a profitable and sustainable venture. As we continue to explore this exciting field, stay with us for more insights into the dynamic interplay between economics and environmental sustainability in lithium battery recycling.
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of lithium battery recycling holds significant promise, driven by continuous technological advancements and growing environmental consciousness. Innovations are not only anticipated to increase recycling efficiency but also to address the diverse chemistries of modern batteries. As electric vehicles become more prevalent, the volume of lithium batteries requiring recycling will surge. By 2030, an estimated 2 million tons of spent lithium-ion batteries are expected to be generated annually, necessitating robust recycling solutions.
Adapting to Evolving Battery Technologies
A key challenge for the recycling industry is the evolving nature of battery technology. Batteries are continuously being optimized for performance, leading to varied compositions and chemistries. This variability requires flexible and adaptable recycling processes capable of handling different types of batteries efficiently.
Navigating Economic and Regulatory Landscapes
Economically, the industry must balance the cost of recycling processes with the value of recovered materials. Additionally, regulatory frameworks will play a crucial role in shaping the recycling industry. Policies that encourage recycling and provide a supportive environment for innovation will be instrumental in driving the industry forward.
We view the future of lithium battery recycling with optimism, recognizing both its potential and the hurdles it faces. The journey ahead involves not only technological innovations but also collaborative efforts among governments, industries, and consumers. By staying at the forefront of these developments, we aim to provide our readers with comprehensive insights into how lithium battery recycling is evolving to meet the demands of a more sustainable future. Join us as we continue to cover the latest trends, challenges, and breakthroughs in this vital field.
Shaping the Future Through Policy and Governance
The role of policy and regulation in shaping the lithium battery recycling industry cannot be overstated. Different countries have implemented various measures to encourage the recycling of batteries. For instance, the European Union has set ambitious targets for battery recycling, mandating that by 2030, 70% of lithium, 95% of cobalt, and 90% of nickel used in batteries must be recycled. In the United States, the introduction of the Battery Material Processing and Battery Manufacturing grant program under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law reflects a growing commitment to support the domestic battery recycling industry.
While policies are essential for promoting sustainable practices, their implementation comes with its own set of challenges. Regulations need to balance the economic viability of recycling processes with environmental and health standards. They also need to keep pace with the rapidly evolving technology in battery manufacturing and recycling.
Techable.com’s Perspective on Policy Impact
We recognize that effective policies and regulations are pivotal in creating a conducive environment for the growth of the lithium battery recycling industry. By incentivizing innovation and ensuring responsible recycling practices, these measures can significantly impact the industry’s development. Our ongoing analysis of policy trends aims to provide our readers with a clear understanding of how governance shapes the future of lithium battery recycling. As we delve deeper into this aspect, stay with us for more insights into the complex interplay between policy, technology, and market dynamics in the world of battery recycling.














0 Comments